A vertical spread options trading strategy where an individual buys and sells two options of the same type (call or put), expiry, and underlying asset, but with different strike prices. The objective is to decrease the amount of premium paid or to hedge existing positions.
Key Points to Consider:
- Vertical spreads are considered limited-risk strategies, as the risk is defined and known upfront, providing traders with a degree of protection against large losses.
- The spreads can be either debit spreads (paying a net premium) or credit spreads (receiving a net premium), depending on whether you buy the lower strike option (debit) or sell it (credit).
- Time decay, also known as theta, affects vertical spreads. The passage of time can be either beneficial or detrimental to the position, depending on whether you are a net buyer or seller of options.
Types of Vertical Spreads
1. Bull Call Spread:
This strategy is used when the trader is moderately bullish on the market. It involves buying a call option at a specific strike price and selling a call option at a higher strike price. The premium received from the sold call offsets the premium paid for the bought call to some extent. The maximum profit is the difference between the two strike prices minus the net premium paid.
2. Bear Call Spread:

This strategy is used when the trader has a moderately bearish outlook on the market. It involves selling a call option at a lower strike price and buying a call option at a higher strike price. The trader profits when the price of the underlying asset falls.
3. Bull Put Spread:
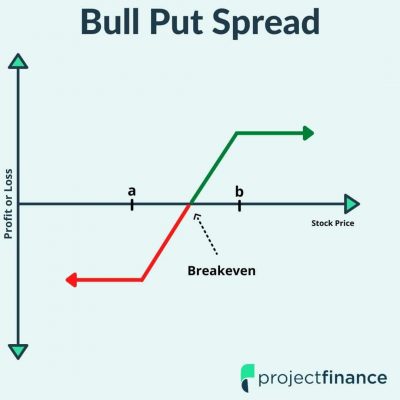
This strategy is used when the trader expects the price of the underlying to rise moderately. It involves selling a put option at a higher strike price and buying a put option at a lower strike price. The maximum profit is the net premium received after setting up the trade.
4. Bear Put Spread:
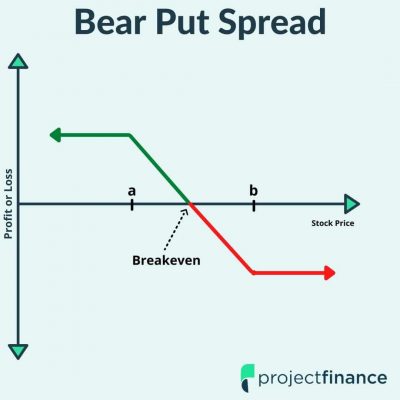
This strategy is used when the trader has a moderately bearish view on the market. It involves buying a put option at a higher strike price and selling a put option at a lower strike price. The maximum profit is the difference between the two strike prices minus the net premium paid.
Advantages of Vertical Spreads
1. Defined Risk:
The maximum potential loss is defined at the onset of the trade. It is the net premium paid for a debit spread or the difference between the strike prices minus the net premium received for a credit spread.
2. Lower Cost:
Compared to buying a standalone option, a spread strategy usually requires less capital because the cost of the bought option is offset by the premium received from the sold option.
3. Flexibility:
Vertical spreads can be constructed to profit from either a bullish or bearish market outlook.
Disadvantages of Vertical Spreads
1. Limited Profit Potential:
The profit potential is capped at the difference between the strike prices for debit spreads and at the premium received for credit spreads.
2. Transaction Costs:
Because spreads involve buying and selling multiple options, the transaction costs can be higher than for single option trades.
3. Requires Greater Market Insight:
Predicting the price range where the underlying asset will stay until expiration can be challenging and requires a nuanced understanding of the market.
Vertical spreads Vs. other option strategies
Vertical spreads and other option strategies each have their unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Here are comparisons between vertical spread techniques and some other common strategies in options trading:
1. Vertical Spread vs Single Options (Long Calls/Puts)
Vertical spreads limit both potential profits and losses compared to buying a single call or put. When you buy a single option, your profit potential is theoretically unlimited, but you could lose the entire premium paid if the market moves against you. On the other hand, in a vertical spread, your profit and loss are both limited.
2. Vertical Spread vs Covered Calls
Covered calls involve holding the underlying asset and selling a call option against it. While covered calls can generate income, they expose you to potential losses if the underlying asset’s price decreases. In contrast, vertical spreads require less capital and limit your potential loss to the net premium paid or received.
3. Vertical Spread vs Straddles and Strangles
Straddles and strangles are strategies used when you expect significant price movement but are unsure of the direction. They involve buying or selling both a call and a put at the same (straddle) or different (strangle) strike prices. These strategies have unlimited profit potential but can also lead to substantial losses. In contrast, vertical spreads provide a more conservative strategy with defined risk and limited profit potential.
4. Vertical Spread vs Iron Condors
An iron condor involves selling a call spread and a put spread on the same underlying asset with the same expiration. This strategy is used when you expect little price movement. While iron condors can provide higher potential income than a single vertical spread, they also require more advanced market knowledge and have higher transaction costs due to the number of options involved.
5. Vertical Spread vs Calendar Spreads
A calendar spread involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying asset and strike price, but with different expirations. This strategy profits from changes in implied volatility and the passage of time. Vertical spreads, on the other hand, are mainly used to profit from directional movements of the underlying asset’s price.
FAQs
Yes, time decay, also known as theta, affects vertical spreads. As time passes, the value of the options may erode, which can be either beneficial or detrimental to the position, depending on whether you are a net buyer or seller of options.
Yes, there are various other options strategies, such as butterfly spreads, iron condors, and straddles, each with its unique risk-reward profile. Traders should explore and understand these strategies before selecting the most suitable one for their market outlook.
Final Thought
This content was created by the help of Redot, Waqar Zakar and Waqar Zaka Trading Group Experts. vertical spreads offer defined risk and are less capital-intensive than some other strategies, they also have limited profit potential and may require more sophisticated market insights. Apart from being careful about the crypto exchange you decade to use, it’s important to choose the strategy that best fits your risk tolerance, market outlook, and investment goals.
